On a beautiful day in early summer, four friends and I decided to picnic and paint in the park. We brought along small squares of watercolour paper split into quadrants, sat in a circle, and took turns painting how we saw each other. These depictions could be abstract or literal: one person did colour swatches of how they interpreted your aura, another person painted objects representing your hobbies and passions. At the end, I got my paper back with four painted interpretations of myself, each done by a different friend.
As I looked at these artistic renderings and considered the close attention my friends had paid me to complete them, I felt a warm swell of emotion and got a little choked up. In that moment, I couldn’t quite define the feeling. It wasn’t exactly joy, nor was it appreciation or pride, but something else. Later, I found the answer in a psychology research paper: it was kama muta.
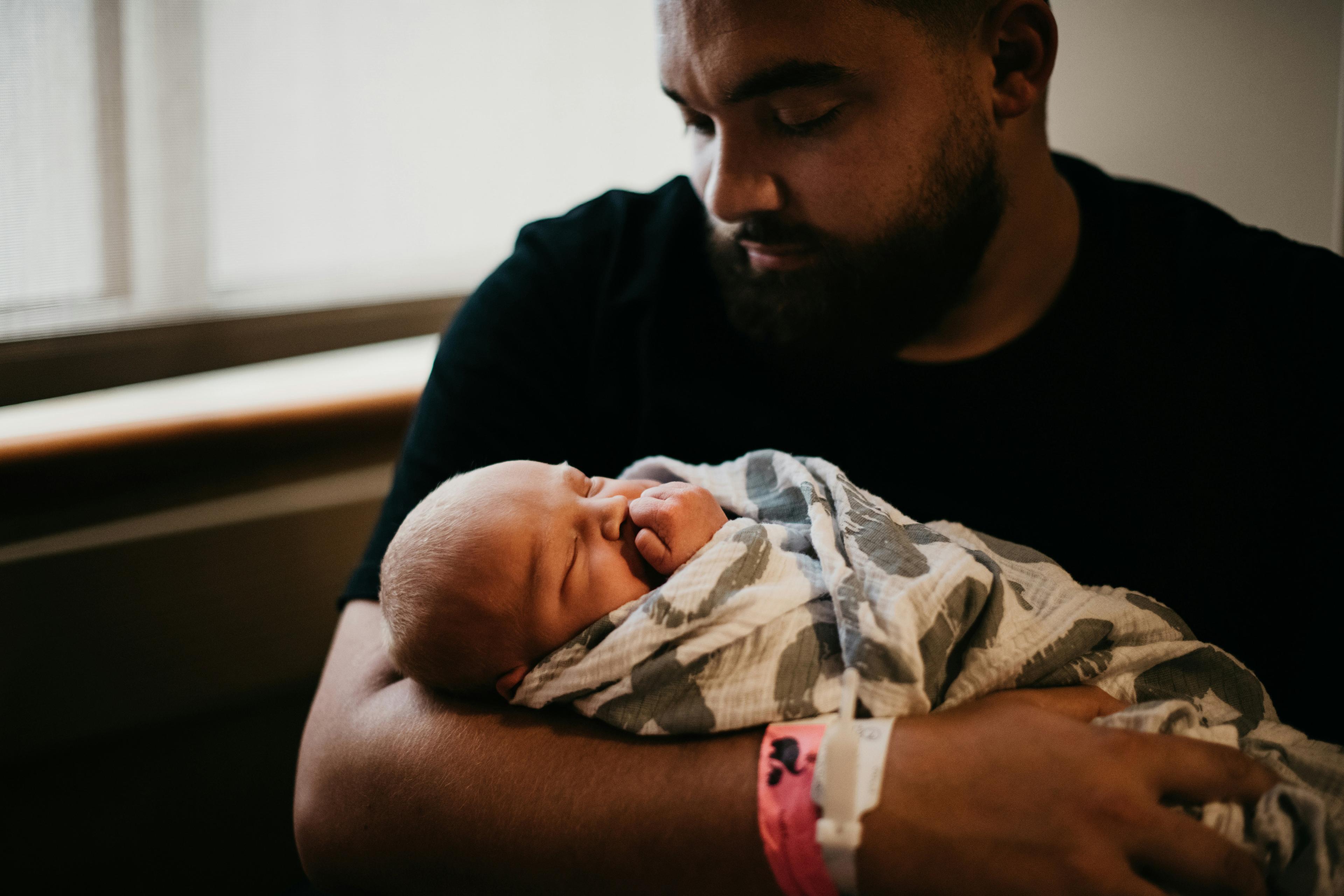
About a decade ago, the anthropologist Alan Fiske saw a gap in the English language. There was no general term for the emotion of being moved or touched by moments of sharing and connection – such as when you hold a baby for the first time, listen to a loved one’s eulogy, or feel profoundly linked to others at a religious or social gathering. Moments like these can produce a warm and fuzzy feeling, sometimes accompanied by tearing up, getting choked up, or the urge to go ‘aww’. Fiske and his colleagues labelled it kama muta, derived from a Sanskrit term that means ‘moved by love’. Experiencing this positive emotional response, they argue, helps to motivate continued engagement in the relationships that spark it.
For me, knowing about the power of kama muta is a useful nudge toward greater bonding in my relationships. Now I look for opportunities to cultivate it where I can, as my friends and I did that day in the park – sharing care and attention so freely that it moved us.